Did you know that by 2025, cybercrime is expected to cost the world over $10.5 trillion annually? With businesses and individuals becoming increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, protecting sensitive information is more crucial than ever. But when discussing protection strategies, two terms often come up: data security and cybersecurity. Are they the same? Not quite.
In this blog post, we’ll break down the differences between data security and cybersecurity, why both are essential, and how you can create a comprehensive security strategy. Plus, we’ll provide you with a Data Security Checklist to help safeguard your business data.
Why It Matters: The Rising Threat Landscape
Cyberattacks and data breaches are on the rise. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 reached $4.45 million—a 15% increase over the last three years. This alarming trend underscores the necessity of proactive security measures to protect both systems and sensitive data.
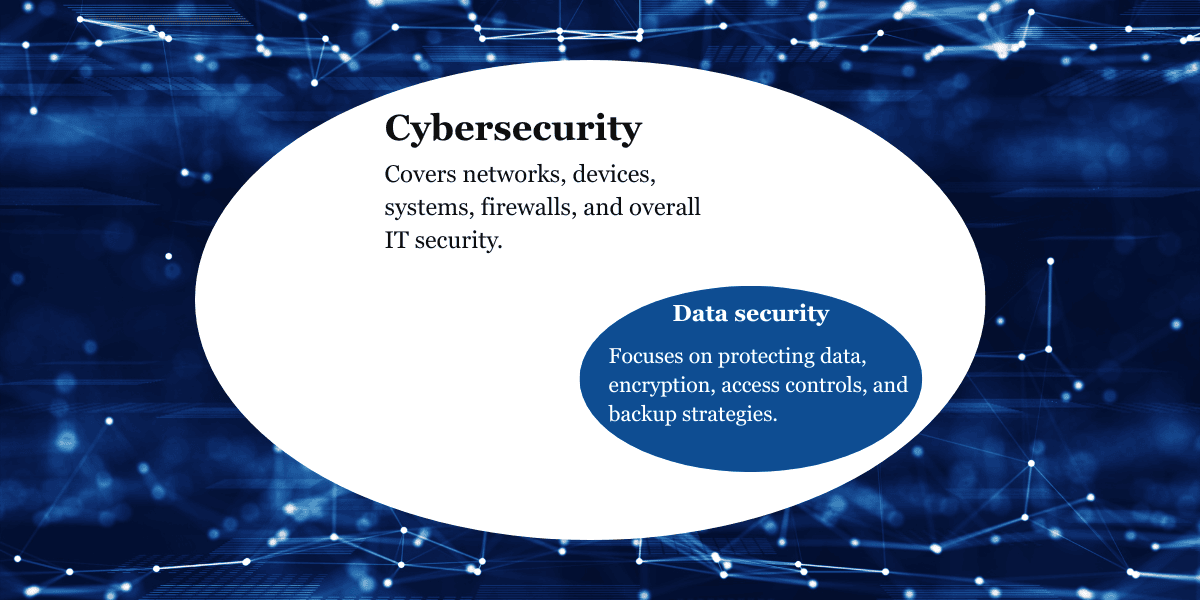
Data Security vs. Cybersecurity: Breaking It Down
1. What is Data Security?
Key Aspects of Data Security:
Encryption: Encoding data so only authorized users can read it.
Access Control: Restricting who can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Masking: Concealing specific data to limit exposure.
Backup & Recovery: Ensuring data is retrievable after a loss or breach.
Compliance & Regulations: Adhering to GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and other laws.
2. What is Cybersecurity?
Key Aspects of Cybersecurity:
Network Security: Preventing unauthorized access to company networks.
Endpoint Protection: Securing devices such as computers, mobile phones, and IoT gadgets.
Firewalls & Intrusion Detection: Blocking malicious traffic and monitoring threats.
Incident Response Plans: Preparing for and mitigating attacks.
Threat Intelligence: Identifying potential cyber threats before they occur.
How They Work Together for Complete Protection
1. A Strong Cybersecurity System Without Data Security is Incomplete
2. Data Security Measures Alone Can’t Prevent Cyber Attacks
3. Compliance & Regulatory Requirements Demand Both
Case Study: The Capital One Data Breach (2019)
A real-world example of why both cybersecurity and data security are crucial is the Capital One data breach. A former employee exploited a misconfigured firewall (a cybersecurity weakness) to access over 100 million customer records. Although the company had data security measures in place, the cybersecurity gap allowed unauthorized access. This breach cost Capital One $190 million in settlements and tarnished its reputation.
Key Takeaway: Had Capital One combined robust cybersecurity with stricter data security measures, this breach could have been prevented.How to Strengthen Your Security Strategy
To ensure comprehensive protection, businesses must integrate both cybersecurity and data security. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
1. Conduct a Security Audit
Evaluate your current security measures. Identify vulnerabilities in networks, applications, and data storage.
2. Implement Layered Security Measures
A multi-layered approach—including firewalls, encryption, access control, and monitoring tools—ensures attackers can’t exploit a single point of failure.
3. Educate Employees
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches. Regularly train employees on phishing scams, password management, and safe data handling.
4. Enforce Access Controls
Limit data access to only those who need it. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
5. Keep Systems & Software Updated
Outdated software is a prime target for cybercriminals. Regularly update systems, apply security patches, and monitor for emerging threats.How to Strengthen Your Security Strategy
In today’s digital world, protecting your business isn’t just about preventing cyberattacks—it’s about securing your data from all angles. While cybersecurity shields your systems, data security ensures your sensitive information remains intact and inaccessible to unauthorized users.
Want to take the next step in securing your data? Book a free Consultation Call to assess and strengthen your data protection strategy today!
